Frequently Asked Questions
What did Volta invent?
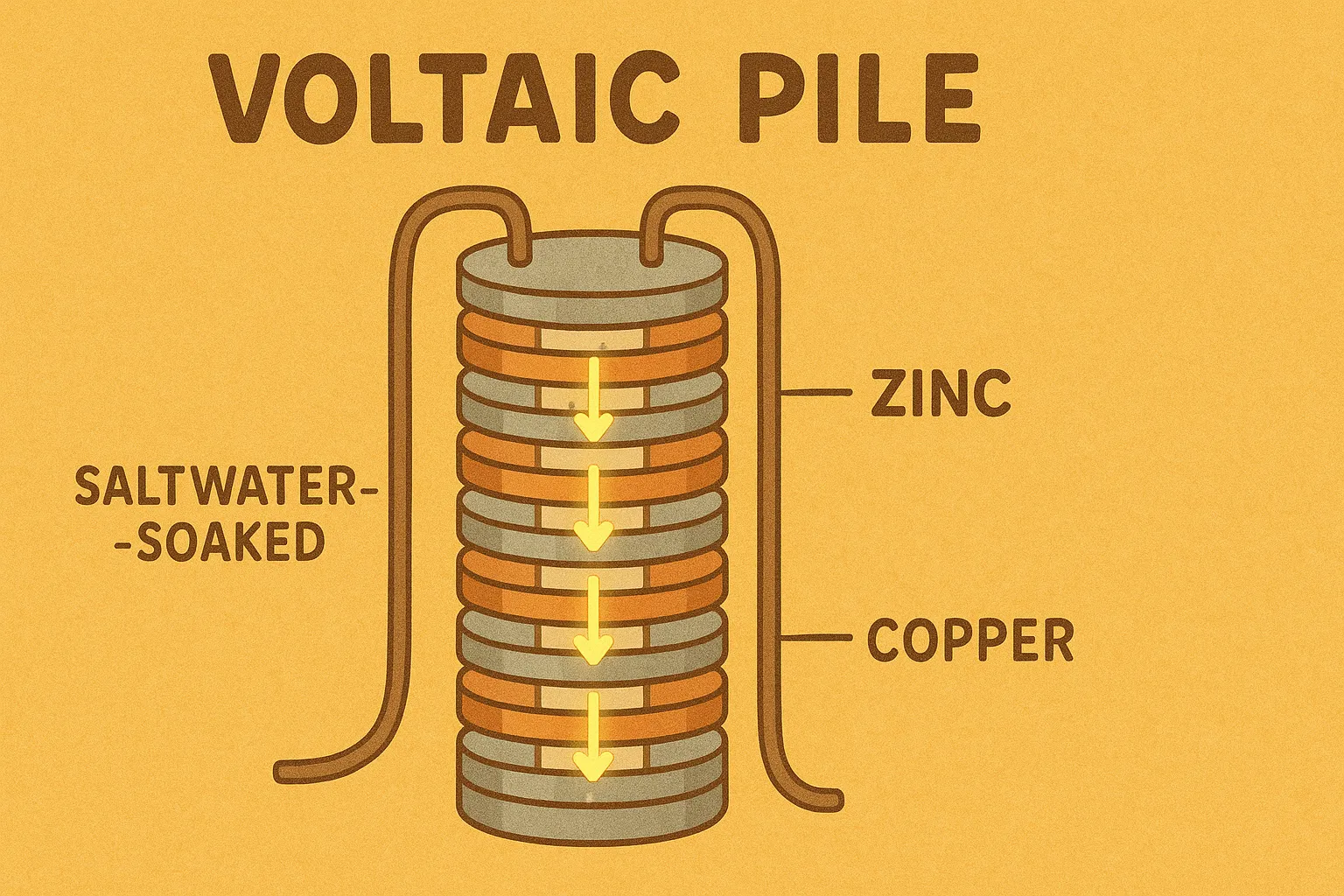
He invented the voltaic pile, the first chemical battery (about 1800), which produced a steady electric current for experiments and practical use.
Why is the unit 'volt' named after him?
Scientists named the unit of electric potential the 'volt' to honor Volta's pioneering work on the battery and electrical potential.
Where was Volta from?
Alessandro Volta was born in Como, Italy, in 1745 and worked in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Did Volta discover methane?
Volta studied marsh gas and demonstrated its flammability; this gas is what we now call methane, part of his early experiments with gases.
How did his battery help the world?
The voltaic pile gave a steady current that let scientists build electric devices and start technologies that eventually led to telegraphs, motors, and modern batteries.