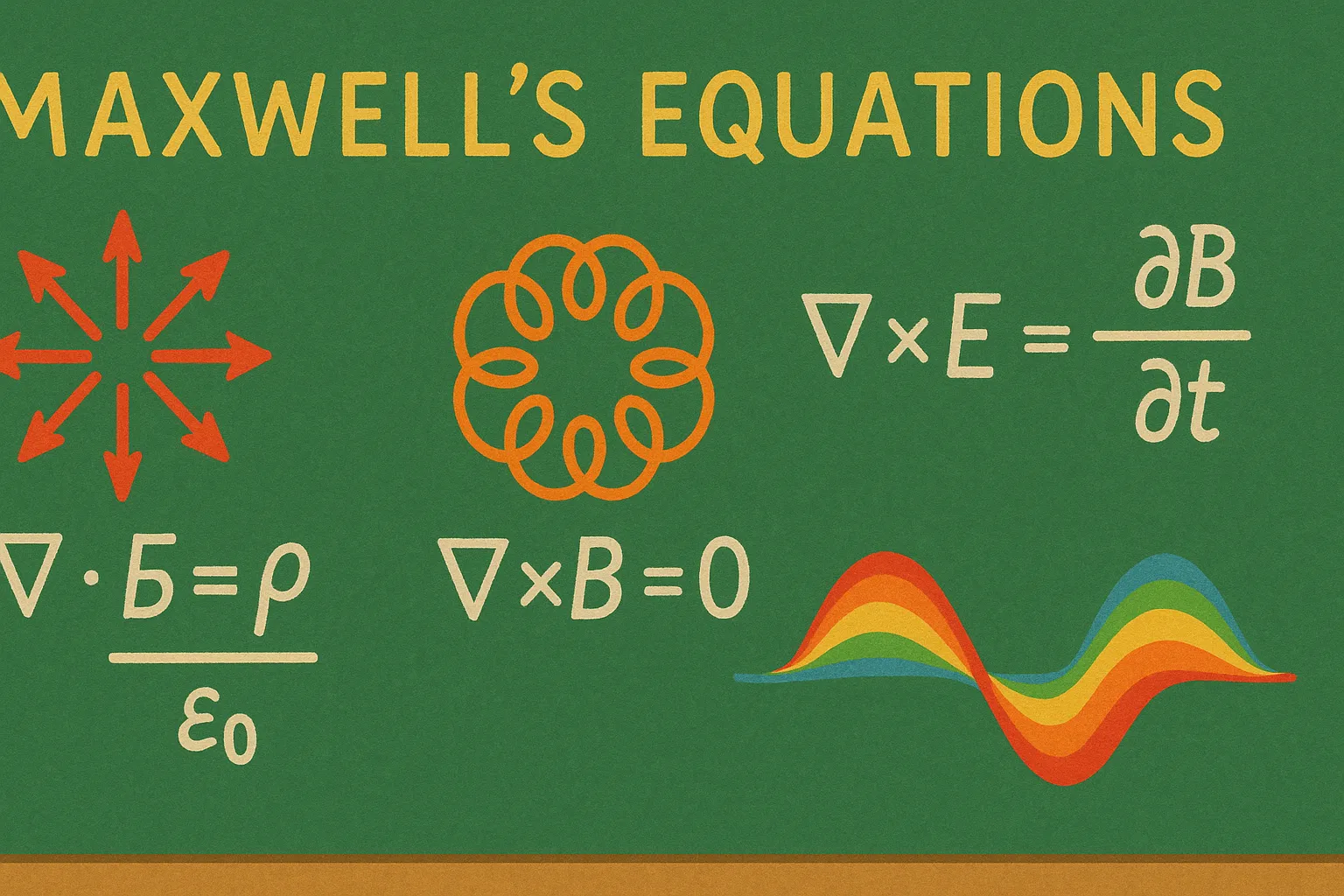James Clerk Maxwell

1831-1879
Unified electricity, magnetism, and light
Publicado: September 21, 2025
Perguntas frequentes
What did Maxwell discover?
He showed electricity and magnetism are linked and that light is an electromagnetic wave; he formulated Maxwell's equations.
When did he live?
James Clerk Maxwell lived from 1831 to 1879 in Scotland during the 19th century.
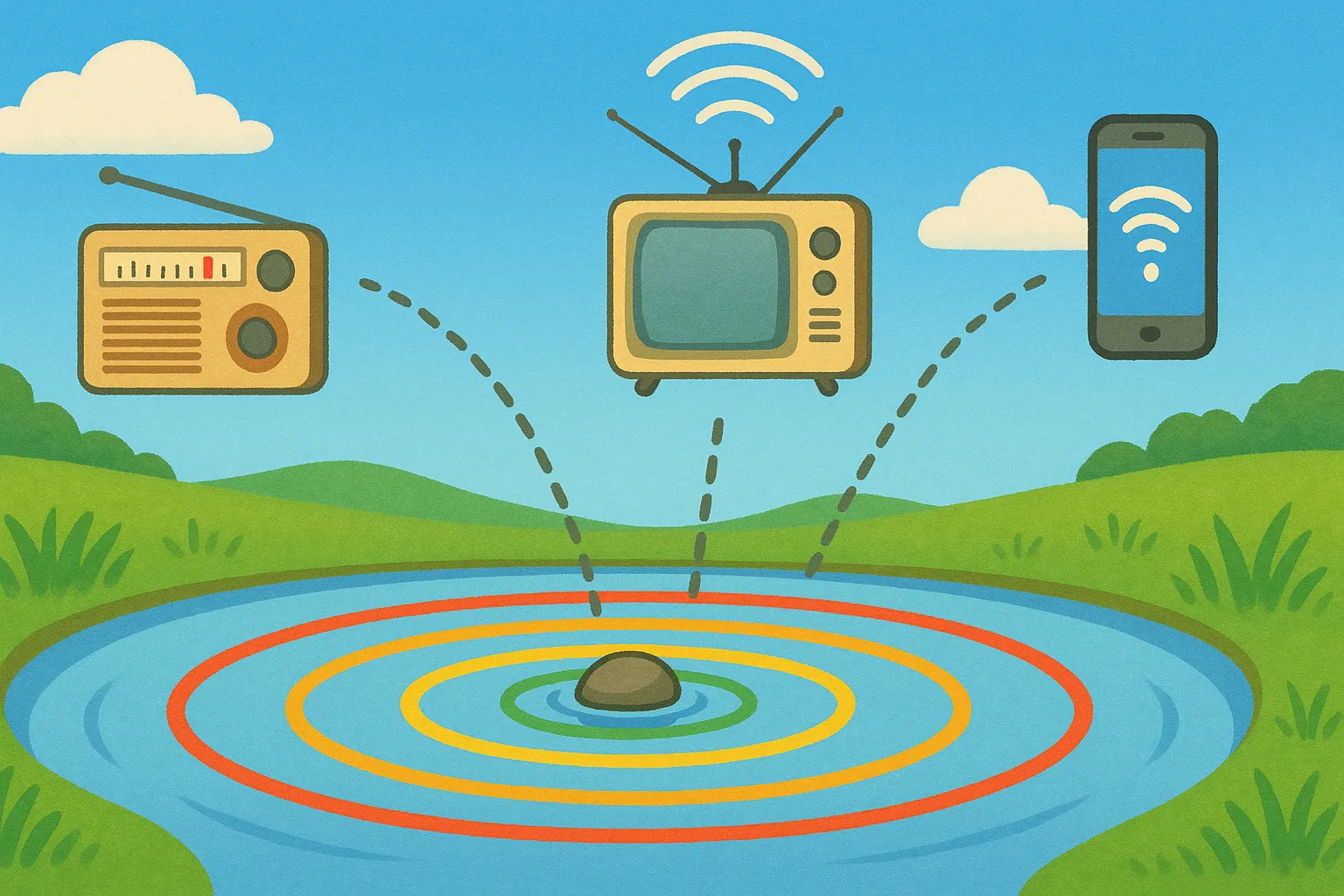
Did Maxwell invent radio?
He predicted electromagnetic waves that made radio possible. He didn't build the first radio, but his theory led later inventors to create radio technology.
What else did he do?
He helped demonstrate the first color photograph and developed important ideas about how gases behave in early kinetic theory.